Aurora NOAA: Your Ultimate Guide To Witnessing Nature's Spectacular Light Show
Let’s dive into the mesmerizing world of auroras and the role NOAA plays in tracking them. If you’ve ever been curious about the dazzling light displays that paint the night sky in vibrant colors, then you’re in the right place. Aurora NOAA is more than just a scientific term; it’s your gateway to understanding one of nature’s most breathtaking phenomena.
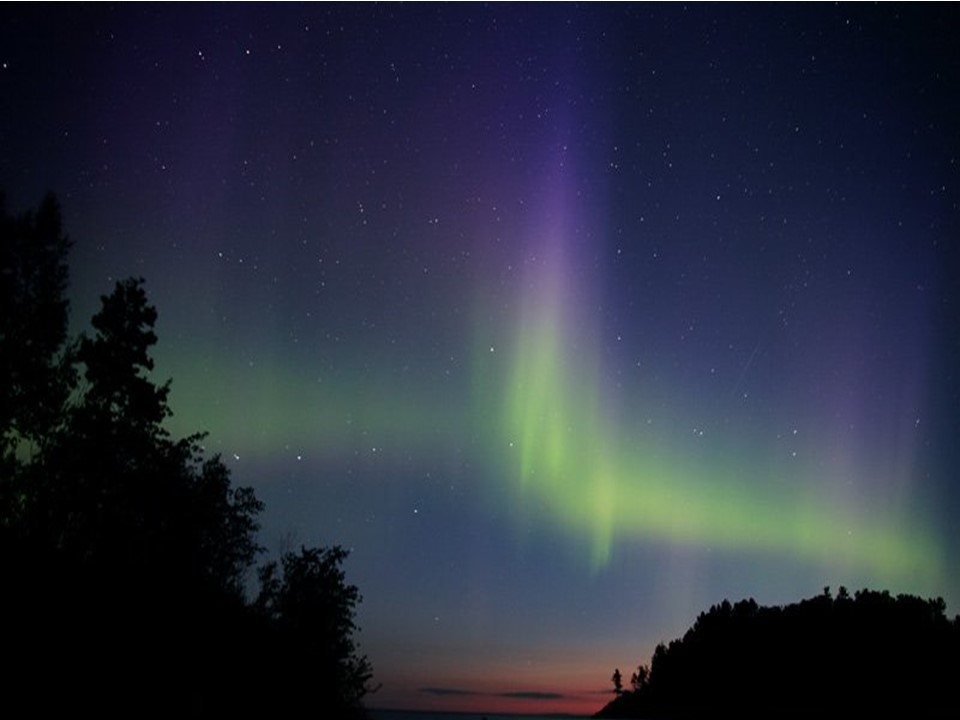
Picture this: you’re standing in the middle of a frozen wilderness, the air crisp and cold, and suddenly the sky comes alive with a dance of greens, purples, and pinks. It’s not a dream—it’s the aurora borealis, and it’s one of the most awe-inspiring sights on Earth. But how do we predict when and where these magical displays will occur? Enter NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which plays a crucial role in monitoring space weather and auroral activity.
Whether you’re a seasoned stargazer or someone who’s just curious about the science behind the auroras, this article will take you on a journey through the wonders of aurora NOAA. From understanding the basics to learning how to plan your aurora hunting adventure, we’ve got you covered. So, grab your favorite beverage, sit back, and let’s explore the electrifying world of auroras together!
Read also:Rouxrouxxx Onlyfans Leak
What Exactly is Aurora NOAA?
Alright, let’s break it down. Aurora NOAA refers to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s efforts to track and forecast auroras, also known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) and southern lights (aurora australis). These natural light shows occur when charged particles from the sun collide with Earth’s atmosphere, creating stunning displays of color in the polar regions.
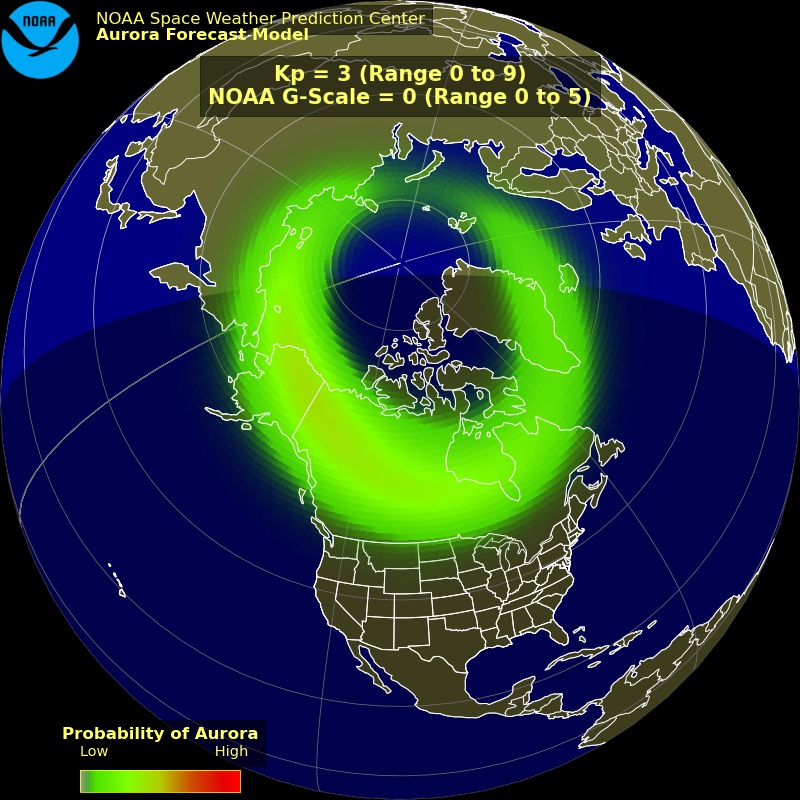
NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) is at the forefront of monitoring these phenomena. By analyzing solar activity, geomagnetic storms, and other factors, scientists can predict when and where auroras are likely to appear. This information is invaluable for aurora enthusiasts, researchers, and even aviation and communication industries that rely on accurate space weather forecasts.
Why Do Auroras Happen?
So, what’s the science behind this celestial magic show? Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty. Auroras occur due to a complex interaction between the sun and Earth’s magnetic field. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Solar Wind: The sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles called the solar wind.
- Earth’s Magnetic Field: When these particles reach Earth, they interact with our planet’s magnetic field, which funnels them toward the polar regions.
- Atmospheric Collision: As the charged particles collide with oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the atmosphere, they release energy in the form of light, creating the vibrant colors we see in the auroras.
It’s like nature’s own lightbulb, powered by the sun and Earth’s magnetic field. Cool, right?
How NOAA Predicts Auroras
Now that we know what causes auroras, let’s talk about how NOAA predicts them. The process involves a combination of satellite observations, ground-based instruments, and advanced computer models. Here’s how it works:
Satellite Monitoring: NOAA operates a fleet of satellites that monitor solar activity and space weather. These satellites provide real-time data on solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and other phenomena that can trigger auroras.
Read also:Celebrity Onlyfans Leak
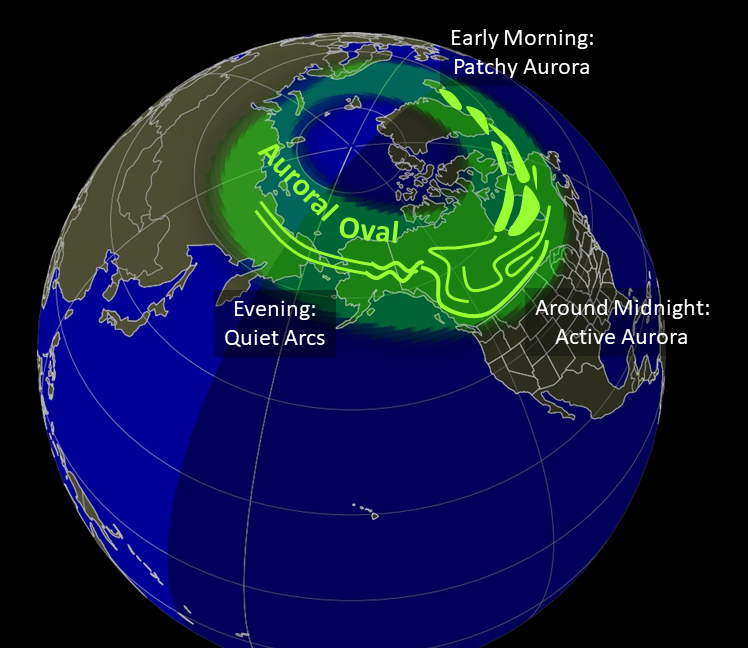
Ground-Based Observations: In addition to satellite data, NOAA relies on ground-based magnetometers and all-sky cameras to track geomagnetic activity and auroral displays. These instruments help scientists pinpoint the location and intensity of auroras.
Forecast Models: Using the data collected from satellites and ground-based instruments, NOAA runs advanced computer models to predict auroral activity. These forecasts are then shared with the public through websites, apps, and other platforms.
Key Factors in Aurora Predictions
There are several key factors that NOAA considers when predicting auroras:
- Solar Wind Speed: Faster solar wind speeds increase the likelihood of auroras.
- Bz Component: This refers to the north-south orientation of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF). A negative Bz value means the IMF is aligned with Earth’s magnetic field, increasing the chances of auroras.
- Kp Index: The Kp index measures geomagnetic activity on a scale of 0 to 9. Higher Kp values indicate stronger auroral activity.
By monitoring these factors, NOAA can provide accurate aurora forecasts that help enthusiasts plan their viewing experiences.
The Best Places to See Auroras
Ready to chase the northern lights? Here are some of the best places to witness auroras:
- Iceland: With its stunning landscapes and minimal light pollution, Iceland is a top destination for aurora hunters.
- Alaska: The Last Frontier offers prime viewing opportunities, especially in remote areas like Fairbanks and Denali National Park.
- Northern Norway: Cities like Tromsø and Svalbard are famous for their aurora displays, thanks to their high latitude and clear skies.
- Sweden and Finland: The Lapland region in both countries provides excellent conditions for aurora viewing.
Remember, timing is everything. The best time to see auroras is during the winter months when the nights are longest and the skies are darkest.
Tips for Aurora Hunting
Here are some tips to enhance your aurora hunting experience:
- Check the Forecast: Use NOAA’s aurora forecasts to plan your trip during periods of high auroral activity.
- Find Dark Skies: Light pollution can diminish the visibility of auroras, so head to remote areas with minimal artificial lighting.
- Be Patient: Auroras can be unpredictable, so be prepared to wait and enjoy the night sky even if the lights don’t appear.
- Stay Warm: Dress in layers and bring extra clothing to stay comfortable in cold temperatures.
With these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to witness the magic of auroras firsthand.
The Science Behind Aurora Colors
Ever wondered why auroras come in so many different colors? It all comes down to the type of gas particles involved in the collision and the altitude at which they occur. Here’s a breakdown:
- Green: The most common auroral color, caused by oxygen molecules at altitudes of around 60 miles.
- Red: Produced by oxygen molecules at higher altitudes, typically above 150 miles.
- Purple and Pink: These colors result from nitrogen molecules at lower altitudes.
- Blue: Rarely seen, blue auroras occur when nitrogen molecules are excited at higher altitudes.
Each color tells a story about the specific conditions in Earth’s atmosphere at the time of the auroral display. Isn’t science amazing?
How Altitude Affects Aurora Colors
The altitude at which auroras occur plays a significant role in determining their colors. Lower-altitude auroras tend to be dominated by green and purple hues, while higher-altitude displays feature more red and blue tones. This variation creates the stunning tapestry of colors that we see in the night sky.
The Importance of Aurora NOAA Forecasts
Why are NOAA’s aurora forecasts so important? For one, they help aurora enthusiasts plan their viewing trips with greater accuracy. But beyond that, these forecasts have practical applications in various industries:
- Aviation: Pilots rely on space weather forecasts to avoid potential disruptions caused by geomagnetic storms.
- Communication: Satellites and radio communications can be affected by solar activity, making accurate forecasts crucial for maintaining reliable communication systems.
- Power Grids: Strong geomagnetic storms can impact power grids, so utility companies use NOAA’s data to prepare for potential outages.
In short, NOAA’s aurora forecasts aren’t just for stargazers—they’re essential for ensuring the safety and functionality of modern technology.
How You Can Use NOAA Forecasts
Here’s how you can make the most of NOAA’s aurora forecasts:
- Visit the NOAA SWPC Website: Check the latest aurora forecasts and Kp index updates.
- Download Aurora Apps: Many apps use NOAA data to provide real-time updates on auroral activity.
- Join Aurora Communities: Connect with fellow enthusiasts who share tips and sightings based on NOAA forecasts.
With these tools at your disposal, you’ll never miss a chance to witness the northern lights.
Conclusion: Your Aurora Adventure Awaits
So there you have it—everything you need to know about aurora NOAA and how to plan your own aurora hunting adventure. From understanding the science behind these mesmerizing displays to utilizing NOAA’s forecasts, you’re now equipped with the knowledge to witness one of nature’s greatest wonders.
Don’t forget to share your aurora experiences with us in the comments below. And if you found this article helpful, be sure to check out our other content on all things space-related. The universe is full of mysteries, and we’re here to help you explore them!
Table of Contents
- Aurora NOAA: Your Ultimate Guide to Witnessing Nature's Spectacular Light Show
- What Exactly is Aurora NOAA?
- Why Do Auroras Happen?
- How NOAA Predicts Auroras
- The Best Places to See Auroras
- The Science Behind Aurora Colors
- The Importance of Aurora NOAA Forecasts
- Conclusion: Your Aurora Adventure Awaits